Template Guidelines
Design Principles
Generic Elements, Segments, and Datasets are organized by layers and fields.
Generic Elements, Segments, and Datasets are structured using Components, which are introduced as layers and fields. Each generic element, segment, or dataset has the capacity to encompass multiple layers, and within each layer, there is the potential for multiple fields to be present. This hierarchical arrangement allows for a flexible and comprehensive organization of data and information.
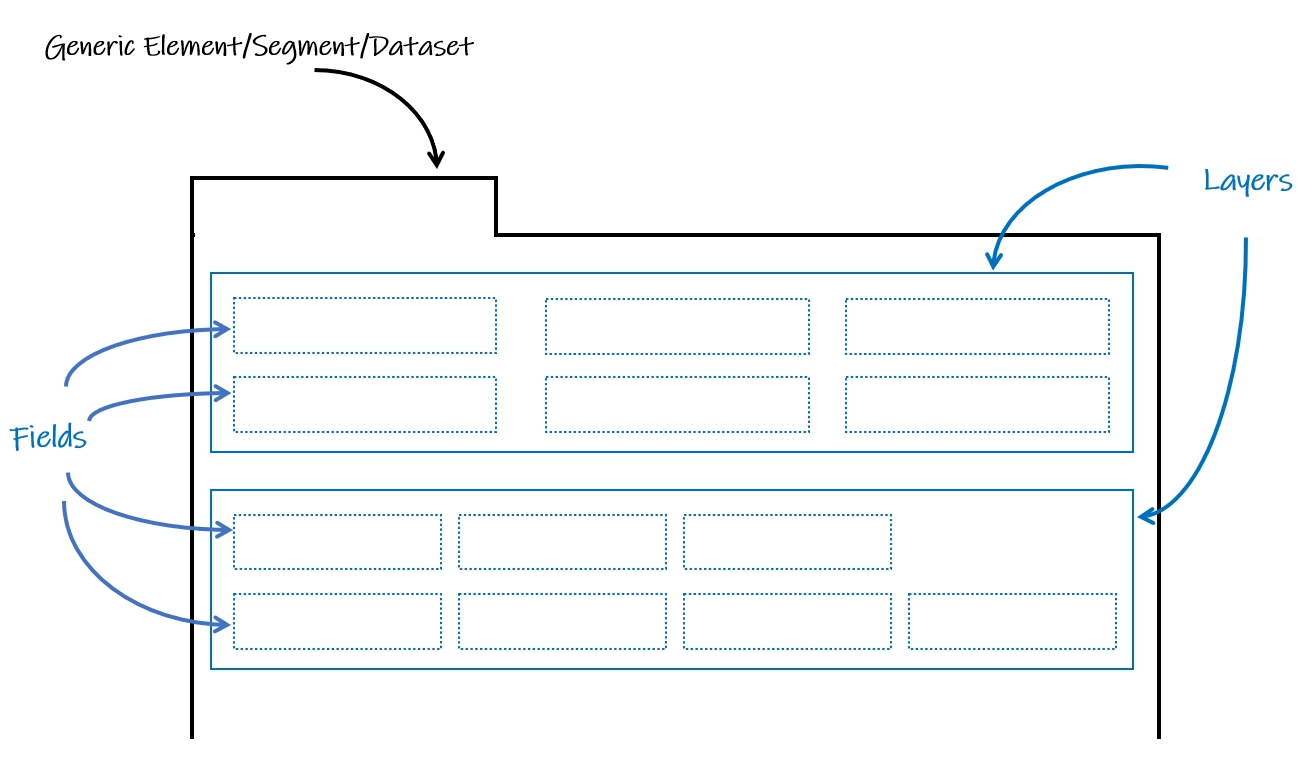
Generic Elements, Segments, and Datasets are structured using Components
What is Element, Segment, Dataset?
In case you are not familiar with the terms Element, Segment, and Dataset, here is a brief overview:
- Element: An element is a fundamental entity which represent an essential aspect within your domain. For example, the sample element or reaction element in Chemotion ELN.
- Segment: A segment is a distinct section that usually has its own identifiable characteristics. You can use it to represent a specific subset of an element.
- Dataset: Within the system, a predefined segment named "Analyses" is provided to capture analysis results. The dataset of the analysis comprises individual data points. Additionally, through Metadata Auto Mapper, metadata extraction from raw files is automatically triggered, facilitating mapping into the dataset.
How do they relate to each other?
This diagram shows how scientists organize research information (processes, materials, devices, datasets) and how these map onto LabIMotion concepts: Generic Element, Generic Segment, and Generic Dataset. It highlights how details and datasets are linked, emphasizing that building blocks can represent experimental structures and analysis layers.
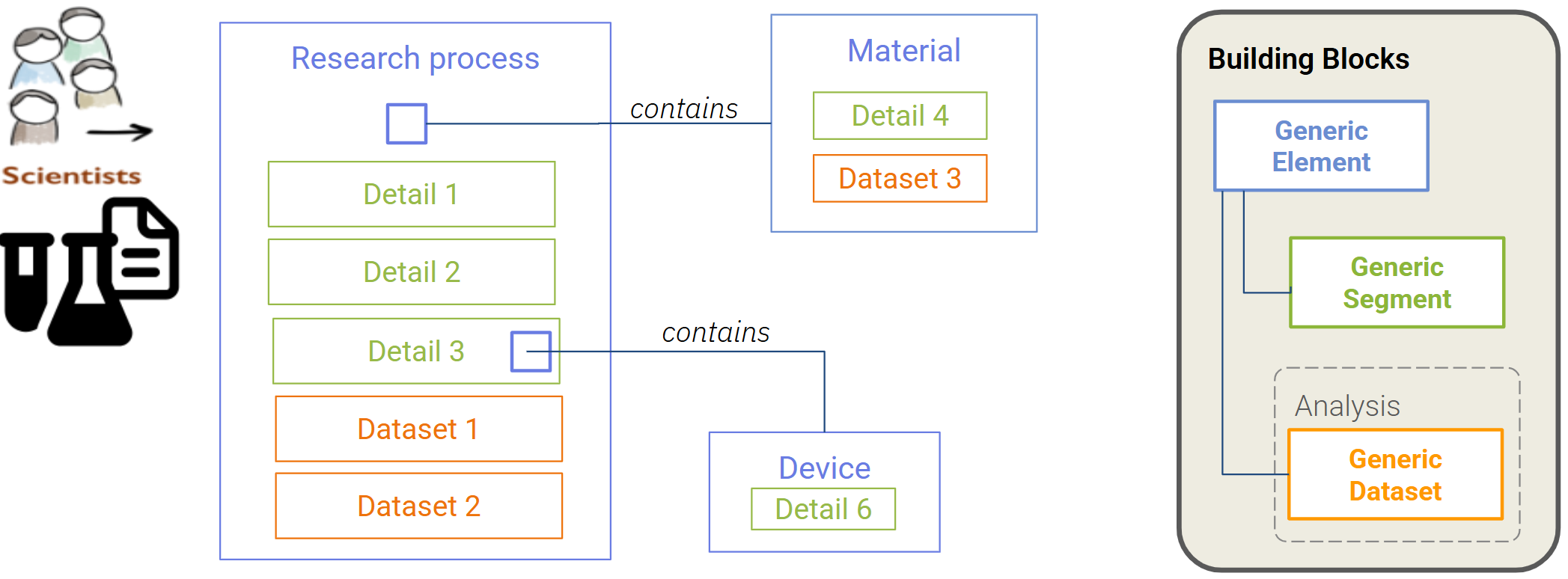
Relationship between LabIMotion building blocks.
How are they structured?
The figure illustrates how templates can be structured at three levels: Element, Segment, and Dataset. Each level can contain multiple layers, and each layer can have multiple fields. This hierarchical structure allows for a flexible and comprehensive organization of data and information.
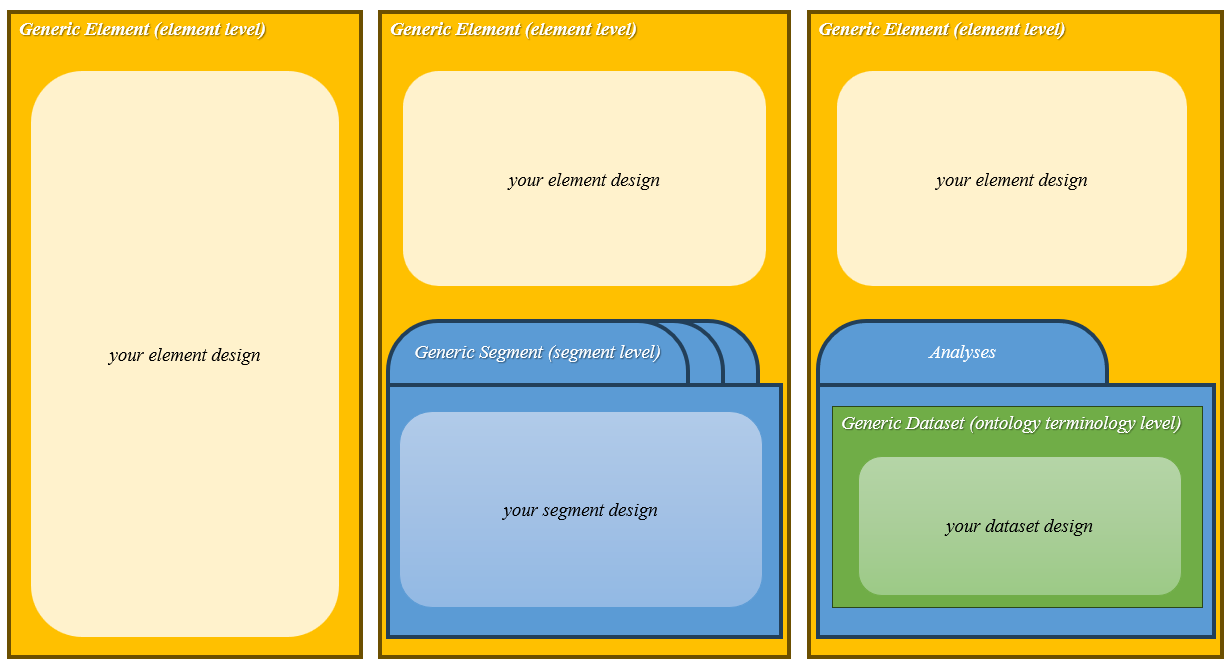
Conceptual overview of LabIMotion design layers
Roles and Resources
🎨 Designer Role
Everything begins with a template - the foundation of the final visualization and output. LabIMotion provides a dedicated tool, Designer, based on a no-code concept that enables a flexible and efficient approach to working directly with outputs. The Designer role is responsible for developing templates that correspond to specific applications and serve as the basis for user interfaces. Explore the Designer Guides to discover the possibilities available to you.
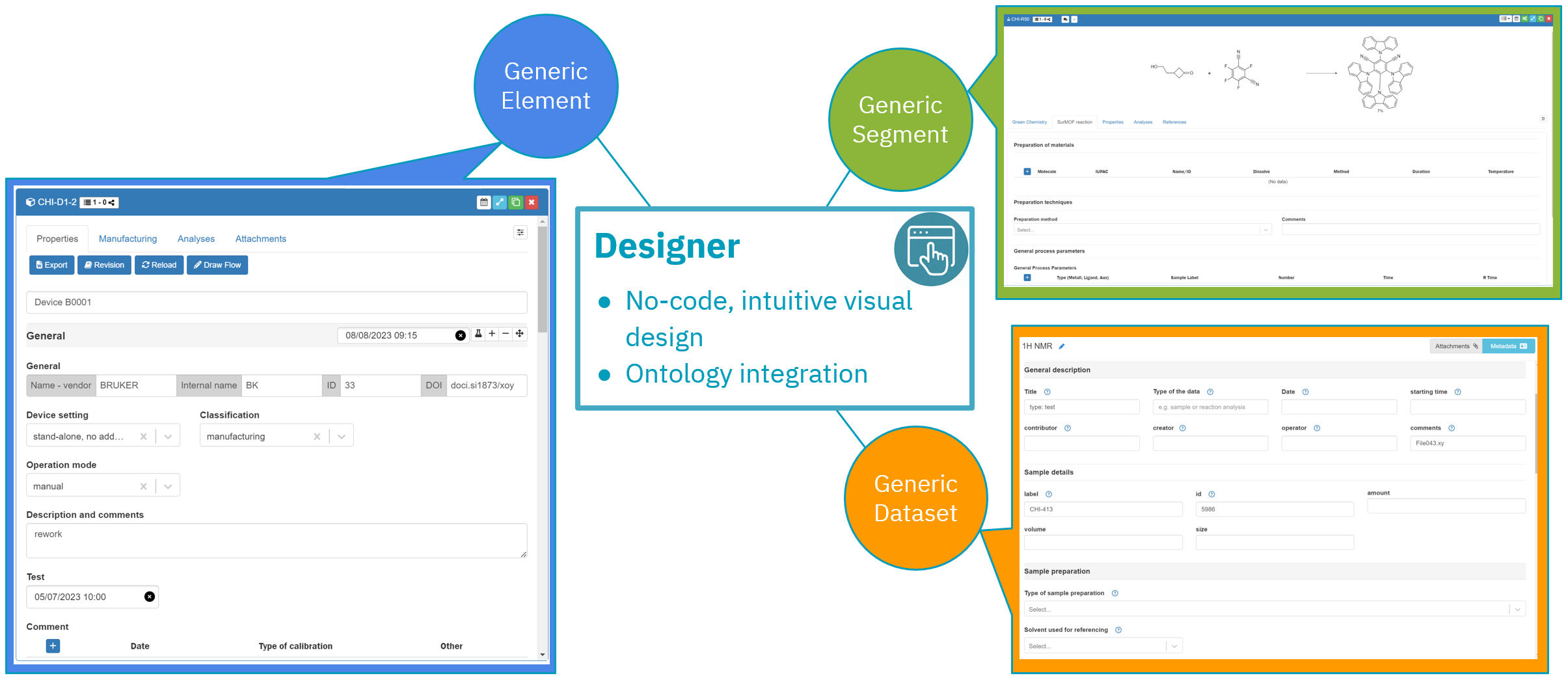
LabIMotion Designer
🔬 User Role
Users are individuals who can choose from a range of pre-designed templates, each meticulously crafted by Designers to suit different applications. Visit the User Guides and delve into the available functionalities.
With the transition from our beta version to the official release version, we're thrilled to introduce a groundbreaking transformation. We have redefined the roles to enhance clarity and streamline user interactions. This new approach divides users into two distinct roles: Designer and User, each with specific responsibilities and permissions tailored to their needs.
📖 Template Hub
Template Hub, is a platform designed to enhance resource sharing and streamline access to invaluable templates contributed by fellow researchers and professionals. The hub serves as a centralized repository where users can discover, share, and collaborate on templates that cater to various scientific applications. By fostering a collaborative environment, the Template Hub empowers users to leverage collective expertise, accelerating research and innovation across disciplines.
Visit LabIMotion Template Hub to explore the resources available.